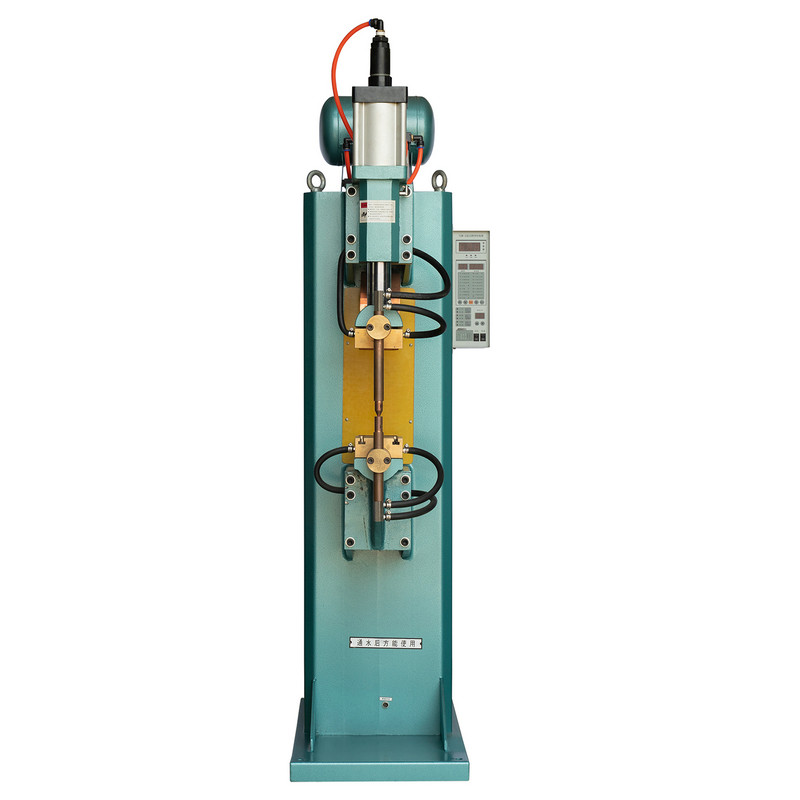
The Stable Performance Butt Welding Machine is a critical equipment in modern pipe processing and industrial welding operations. Its reliability and consistent output largely depend on proper maintenance practices. For manufacturers and workshop managers, understanding the maintenance requirements is essential to ensure high-quality welds, minimize downtime, and prolong machine lifespan.
Understanding the Structure and Function of Stable Performance Butt Welding Machine
Before discussing maintenance requirements, it is essential to understand the basic structure and functions of the Stable Performance Butt Welding Machine. The machine primarily consists of a hydraulic clamping system, heating element, control system, and alignment mechanisms. Each component plays a crucial role in achieving precise butt welds:
- The hydraulic clamping system secures pipes during welding, ensuring correct alignment and pressure.
- The heating element enables consistent thermal fusion of pipe ends.
- The control system regulates welding parameters, monitors pressure, and manages heating cycles.
- The alignment mechanisms guarantee accurate pipe positioning, preventing weld defects.
Proper maintenance of these components ensures Stable Performance Butt Welding Machine operates within optimal parameters and consistently produces high-quality welds.
Daily Maintenance Practices
Daily maintenance is the first line of defense against operational issues. Operators are advised to perform routine inspections and minor adjustments before and after each welding cycle. Key daily maintenance activities include:
- Visual Inspection of Machine Components: Check for wear, damage, or misalignment in the hydraulic clamping system, rails, and moving parts. Loose bolts or connections should be tightened immediately.
- Cleaning Welding Surfaces and Heating Elements: Residual metal, dirt, or oil can affect heat transfer and weld quality. Cleaning with a non-abrasive cloth or brush is recommended.
- Hydraulic Fluid Check: Inspect fluid levels and check for contamination or leaks. Low or contaminated hydraulic fluid can reduce clamping efficiency and impact weld strength.
- Control Panel Monitoring: Ensure all sensor readings, timers, and pressure gauges function correctly. Malfunctioning indicators can lead to improper welding parameters.
Daily maintenance ensures the Stable Performance Butt Welding Machine operates smoothly and prevents minor issues from escalating into costly repairs.
Weekly and Monthly Maintenance Requirements
Beyond daily checks, weekly and monthly maintenance focuses on more in-depth inspection and calibration. These practices help maintain machine precision and extend component lifespan.
Weekly Maintenance
- Lubrication of Moving Parts: All guide rails, clamping arms, and rotating elements should be lubricated using appropriate industrial-grade lubricants.
- Hydraulic System Check: Inspect hydraulic hoses, seals, and valves for leaks or wear. Ensure hydraulic pressure settings are within the manufacturer-recommended range.
- Electrical Connections: Check wires, terminals, and connectors for loose connections or wear. Faulty connections may affect control system stability.
Monthly Maintenance
- Calibration of Pressure and Heating Systems: Verify that clamping pressure and heating temperature match the specified values for different pipe sizes.
- Alignment Verification: Inspect pipe alignment guides and adjust mechanisms to ensure weld accuracy.
- Safety Device Inspection: Test emergency stop functions, protective covers, and warning alarms to ensure operational safety.
The following table summarizes key daily, weekly, and monthly maintenance tasks:
| Maintenance Interval |
Key Activities |
Purpose |
| Daily |
Visual inspection, cleaning heating surfaces, hydraulic fluid check, control panel monitoring |
Prevent immediate operational issues, ensure weld quality |
| Weekly |
Lubrication, hydraulic hose inspection, electrical connection check |
Maintain precision, reduce component wear |
| Monthly |
Calibration of pressure and heating, alignment verification, safety device inspection |
Ensure long-term reliability, operational safety |
Preventive Maintenance Strategies
Preventive maintenance is crucial for minimizing unplanned downtime and optimizing machine performance. Unlike routine checks, preventive strategies involve scheduled interventions based on machine usage patterns and operating conditions.
- Scheduled Component Replacement: Replace wear-prone parts, such as clamping pads, heating elements, and seals, based on manufacturer-recommended intervals or observed wear levels.
- Hydraulic Fluid Replacement: Conduct periodic hydraulic fluid changes to prevent contamination, which can degrade performance and damage components.
- Control System Software Updates: If the Stable Performance Butt Welding Machine includes programmable controllers, update software and perform diagnostics to ensure optimal functionality.
- Thermal System Maintenance: Inspect heating plates for uniformity and replace them if hotspots or uneven heating are detected.
A preventive maintenance schedule should be documented and accessible to all operators and technicians. Proper record-keeping allows for performance tracking and early identification of potential issues.
Common Operational Issues and Their Maintenance Solutions
Even with diligent maintenance, certain operational challenges may arise. Understanding their causes and appropriate maintenance responses is essential for Stable Performance Butt Welding Machine operators.
Common Issues
- Uneven Welds: Often caused by misalignment, inconsistent heating, or improper clamping pressure.
- Hydraulic Leakage: Can occur due to worn seals, loose fittings, or contaminated fluid.
- Electrical Malfunctions: Sensor failures, loose connections, or software errors may affect operation.
- Surface Contamination: Residual metal or dirt on heating plates can compromise weld quality.
Maintenance Solutions
| Issue |
Maintenance Action |
| Uneven welds |
Adjust alignment guides, verify pressure settings, clean heating plates |
| Hydraulic leakage |
Inspect and replace worn seals, check fittings, replace contaminated fluid |
| Electrical malfunctions |
Tighten connections, test sensors, update control software |
| Surface contamination |
Clean heating surfaces with recommended non-abrasive materials |
Proactive maintenance of these areas ensures consistent output and reduces the likelihood of production downtime.
Environmental and Operational Considerations
The operating environment significantly affects the maintenance requirements of Stable Performance Butt Welding Machine. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and dust levels can accelerate wear and reduce equipment efficiency. Recommendations include:
- Controlled Environment: Operate the machine in a well-ventilated and dust-free area.
- Temperature Regulation: Avoid exposing the machine to extreme temperatures that may affect hydraulic fluid viscosity and heating plate performance.
- Routine Environmental Cleaning: Keep surrounding areas free from debris that could interfere with machine operation.
By controlling environmental factors, operators can extend the lifespan of critical components and maintain weld quality.
Advanced Maintenance Practices
For industrial facilities with high throughput, adopting advanced maintenance strategies can significantly enhance machine reliability:
- Condition Monitoring: Implement sensor-based monitoring to track vibration, temperature, and pressure in real time.
- Predictive Maintenance: Use operational data to predict component wear and schedule maintenance before failures occur.
- Operator Training: Regular training ensures operators understand maintenance protocols and best practices for Stable Performance Butt Welding Machine.
These practices not only reduce downtime but also enhance safety and operational efficiency.
Summary of Key Maintenance Requirements
In summary, the maintenance of Stable Performance Butt Welding Machine involves:
- Daily inspections and cleaning to prevent immediate issues.
- Weekly and monthly checks of lubrication, calibration, and safety systems.
- Preventive maintenance strategies including component replacement and fluid management.
- Environmental control to reduce wear and contamination.
- Advanced monitoring and predictive maintenance for industrial applications.
Following these practices ensures long-term machine stability, high weld quality, and operational efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: How often should the hydraulic fluid be replaced in a Stable Performance Butt Welding Machine?
A1: Hydraulic fluid should be replaced according to the manufacturer’s recommendation or if contamination is detected during inspections. For high-usage machines, a replacement every 6-12 months is common.
Q2: What is the best way to clean the heating surfaces?
A2: Use a non-abrasive cloth or brush to remove residual metal, dust, and oil. Avoid using harsh chemicals that could damage the surface coating.
Q3: How can operators detect misalignment early?
A3: Regular checks of alignment guides and visual inspection of clamped pipes before welding help detect misalignment. Sensor readings on the control system can also indicate potential deviations.
Q4: Are there any risks of operating the machine in high humidity?
A4: Yes, high humidity can cause corrosion on metallic components and affect hydraulic system performance. Using a dehumidified or climate-controlled environment is recommended.
Q5: How critical is operator training for maintenance?
A5: Proper training ensures operators understand preventive measures, can identify early signs of wear, and maintain Stable Performance Butt Welding Machine according to safety and operational standards.
References
- Industrial Welding Equipment Maintenance Handbook, 2022 Edition.
- Pipe Fabrication and Butt Welding Techniques, Engineering Press, 2021.
- Hydraulic Systems and Control in Welding Machinery, Technical Publications, 2020.