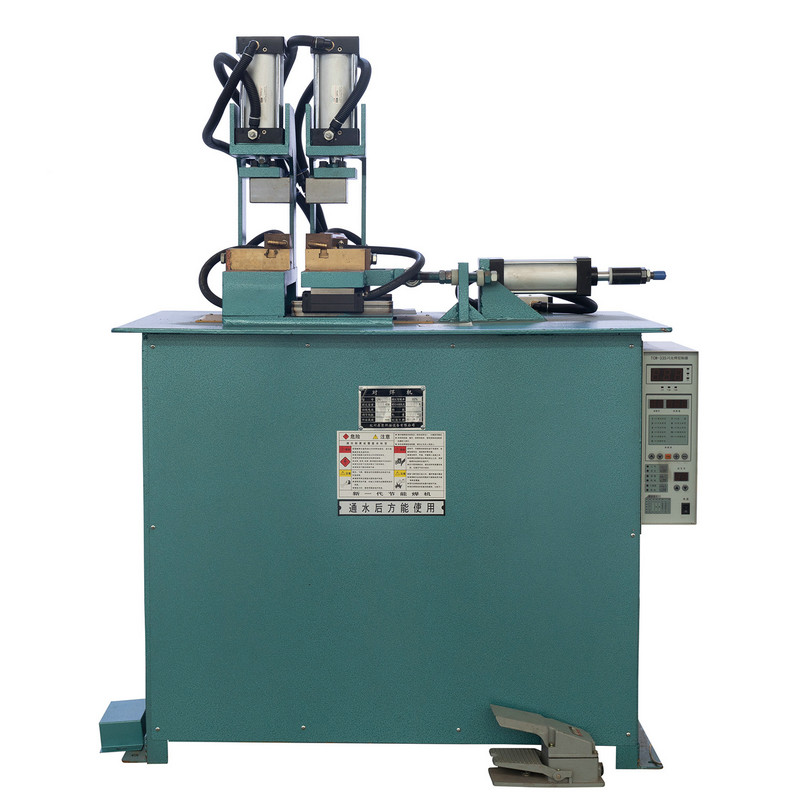
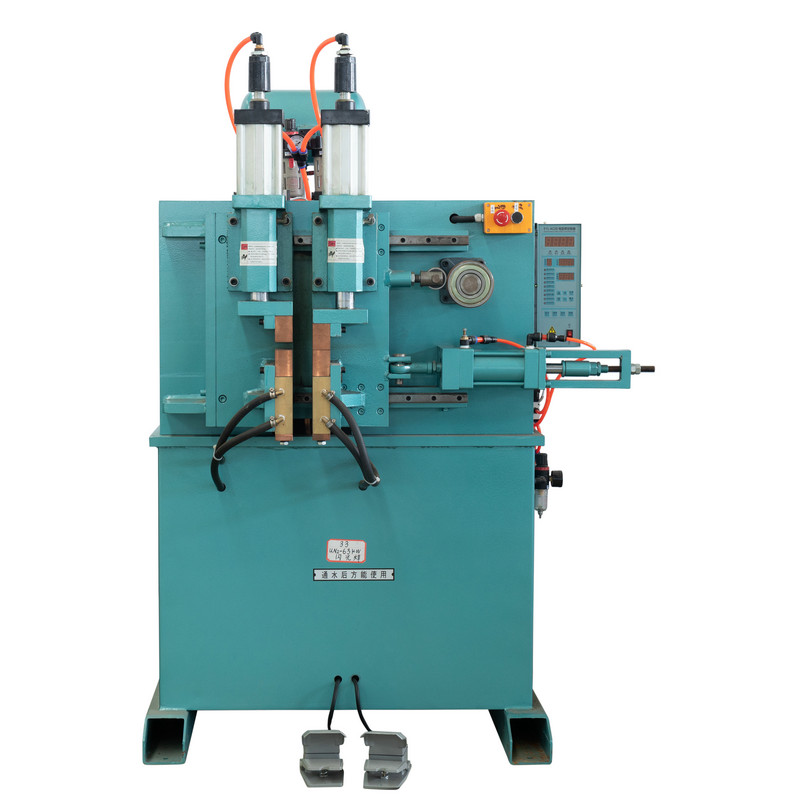
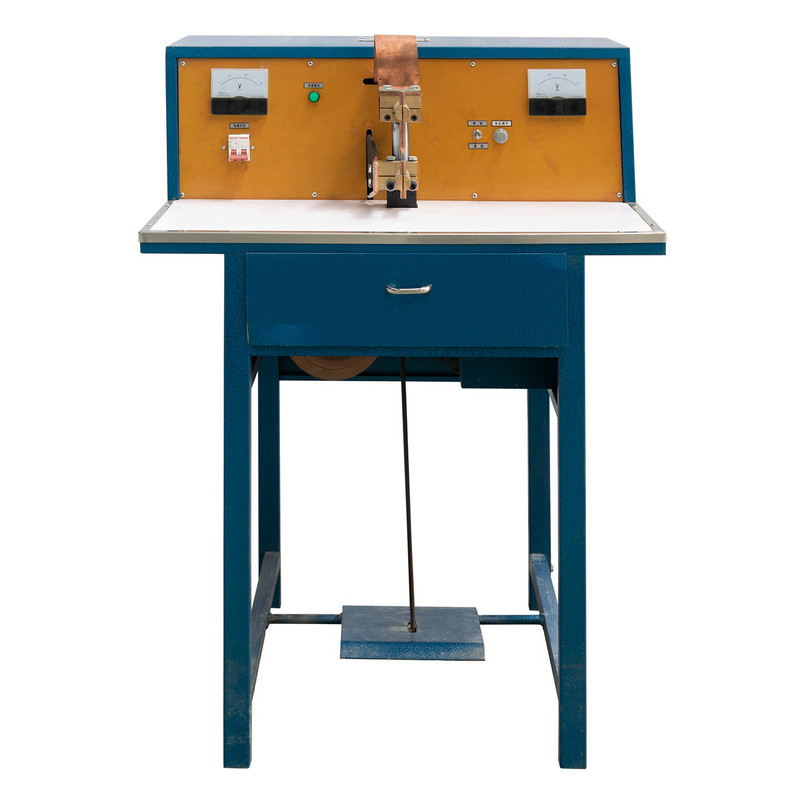
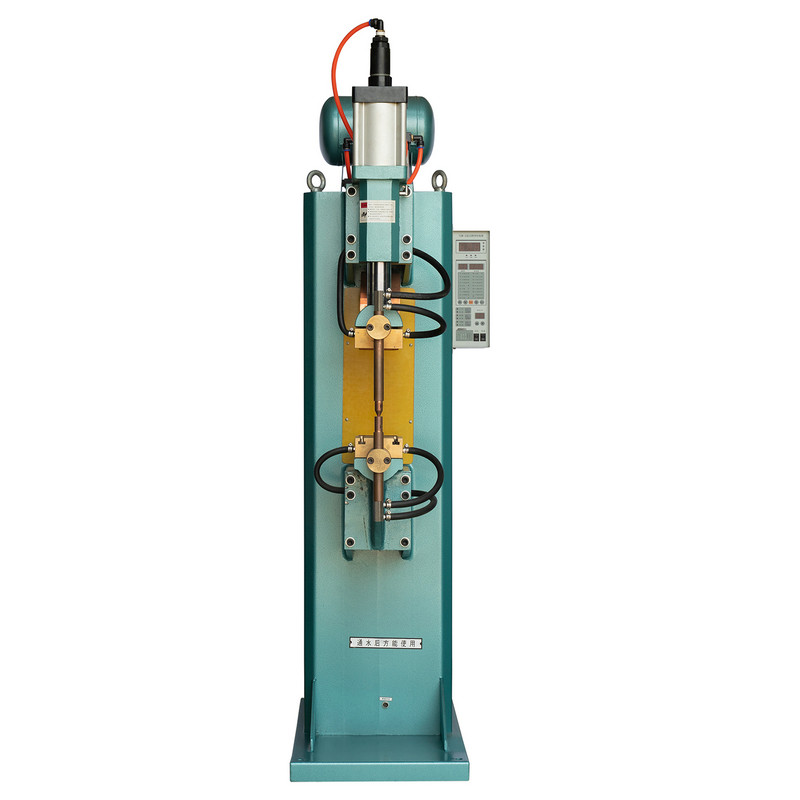
The DN pedal spot welding machine is a widely used tool in metal fabrication, automotive repair, and industrial manufacturing. Its foot-operated mechanism allows for precise control, making it suitable for various welding applications. However, like any mechanical equipment, it can encounter operational issues that affect performance. Understanding these common problems and their solutions ensures consistent weld quality, prolongs machine lifespan, and minimizes downtime.
1. Electrical Issues and Power Supply Problems
One of the most common issues with the DN pedal spot welding machine is electrical failure. Operators may experience a complete loss of power, intermittent operation, or weak welding output. These problems often stem from faulty wiring, blown fuses, or improper voltage supply.
First, check the power source to ensure the machine is receiving the correct voltage. Low voltage can lead to insufficient current flow, resulting in weak or incomplete welds. If the machine fails to turn on, inspect the power cord and connections for damage. Loose or corroded terminals can disrupt electrical flow and should be cleaned or replaced.
Another frequent electrical issue is a tripped circuit breaker or blown fuse. The DN pedal spot welding machine draws significant current, and an overload can cause protective components to fail. Replacing a blown fuse or resetting the breaker may resolve the issue, but recurring failures indicate a deeper problem, such as a short circuit or defective transformer.
If the machine powers on but does not generate sufficient heat, the issue may lie in the transformer or secondary welding circuit. A malfunctioning transformer often requires professional servicing, while damaged cables or loose connections can be repaired by the operator.
2. Electrode Wear and Degradation
The electrodes in a DN pedal spot welding machine endure extreme heat and pressure, leading to gradual wear. Over time, this wear causes deformation, pitting, or contamination, resulting in poor weld quality. Common symptoms include inconsistent weld nuggets, sticking electrodes, or excessive sparking.
Regular inspection and maintenance of electrodes are crucial. If the electrode tips are mushroomed or pitted, they should be dressed (reshaped) using a file or electrode dressing tool. Severe wear necessitates replacement to ensure proper current conduction.
Contamination is another concern, as oil, rust, or coatings on workpieces can transfer to the electrodes, increasing resistance and reducing efficiency. Cleaning the electrodes with a wire brush or emery cloth helps maintain conductivity. In some cases, using anti-spatter spray can minimize buildup.
Electrode misalignment can also cause uneven pressure distribution, leading to weak welds. Adjusting the electrode holder or realigning the arms ensures uniform contact with the workpiece.
3. Inconsistent or Poor-Quality Welds
A recurring issue with the DN pedal spot welding machine is inconsistent weld strength, which may manifest as weak joints, partial fusion, or excessive indentation. Several factors contribute to this problem, including incorrect pressure settings, improper current adjustment, or poor workpiece preparation.
First, verify that the welding pressure is properly adjusted. Insufficient pressure prevents proper metal fusion, while excessive pressure can deform the workpiece. The foot pedal should provide smooth and consistent force application.
Current settings must match the material thickness and type. Thin materials require lower current to avoid burn-through, whereas thicker metals need higher amperage for sufficient penetration. If welds are inconsistent, recalibrating the current control may be necessary.
Workpiece cleanliness is another critical factor. Rust, paint, or grease on the metal surface increases electrical resistance, leading to poor fusion. Cleaning the welding area with a degreaser or abrasive material improves conductivity.
4. Mechanical Malfunctions and Pedal Operation Issues
The foot pedal mechanism in the DN pedal spot welding machine is essential for controlling welding pressure and timing. If the pedal feels stiff, unresponsive, or fails to return to its original position, mechanical issues may be present.
Lubrication of the pedal hinge and linkage points can resolve stiffness caused by friction or rust buildup. If the pedal does not spring back, inspect the return spring for damage or fatigue and replace it if necessary.
Misalignment in the welding arms or loose pivot points can also affect performance. Tightening bolts and ensuring smooth movement of mechanical components prevents erratic operation.
5. Overheating and Cooling System Problems
Prolonged use of the DN pedal spot welding machine can lead to overheating, especially if duty cycles are exceeded. Overheating damages internal components, reduces electrode life, and degrades weld quality.
Ensure the machine is operated within its recommended duty cycle, allowing sufficient cooling time between welds. If overheating persists, check for blocked ventilation or a malfunctioning cooling fan. Cleaning dust and debris from cooling vents improves airflow.
In water-cooled models, inspect the coolant level and circulation system for leaks or blockages. Low coolant levels or pump failures can cause rapid overheating.
The DN pedal spot welding machine is a reliable tool, but like any equipment, it requires proper maintenance and troubleshooting to function optimally. Electrical faults, electrode wear, inconsistent welds, mechanical issues, and overheating are common challenges that operators may encounter. By following systematic troubleshooting steps—such as checking power supply, maintaining electrodes, adjusting settings, and ensuring mechanical integrity—users can minimize downtime and achieve consistent welding performance.
Regular inspection and preventive maintenance are key to extending the machine’s lifespan and ensuring high-quality welds in industrial and workshop environments.
Quick Troubleshooting Reference Table
| Issue |
Possible Cause |
Solution |
| No power |
Blown fuse, loose wiring |
Check/replace fuse, secure connections |
| Weak welds |
Low current, dirty electrodes |
Adjust amperage, clean/dress electrodes |
| Sticking electrodes |
Contamination, excessive heat |
Clean tips, use anti-spatter spray |
| Overheating |
Excessive duty cycle, poor cooling |
Allow cooling time, check ventilation |
| Pedal stiffness |
Lack of lubrication, spring failure |
Lubricate hinges, replace spring |
This structured approach ensures efficient diagnosis and resolution of common issues, keeping the DN pedal spot welding machine in optimal working condition.