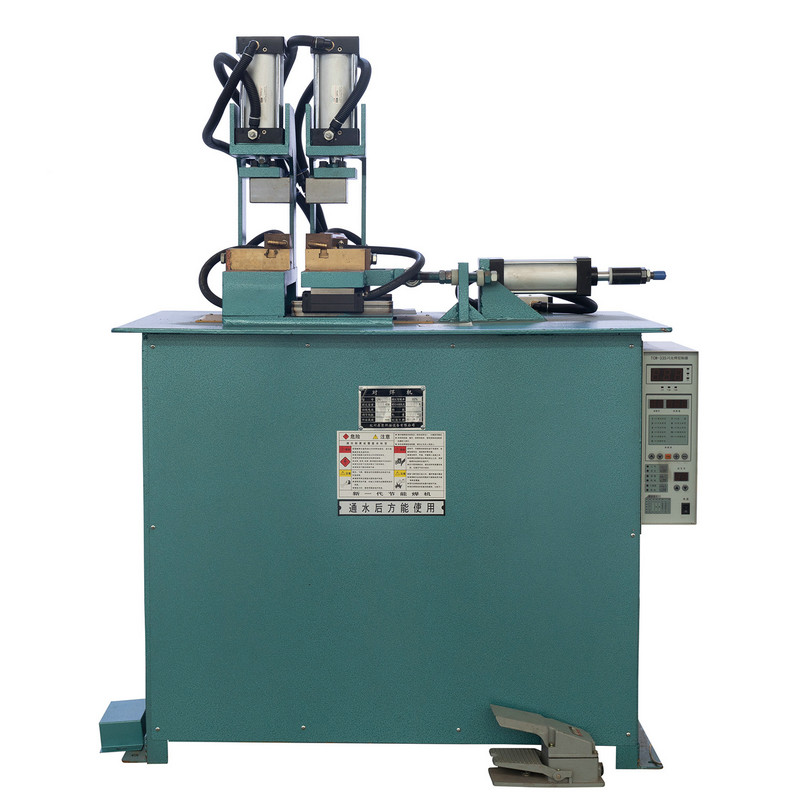
The foot-operated steel bar butt welding machine has become an essential tool in the construction and manufacturing industries. Known for its efficiency in joining steel bars, its durability directly affects workflow continuity, safety, and cost efficiency.
Material quality and manufacturing standards
The durability of a foot-operated steel bar butt welding machine starts with the materials used in its construction. Machines built with high-grade steel and durable alloys tend to withstand repeated stress, pressure, and temperature fluctuations better than those made from lower-quality metals. Additionally, the precision in manufacturing plays a vital role. Machines produced with accurate alignment and tight tolerances exhibit less wear and tear, reducing the likelihood of mechanical failures over time.
In addition to metals, other components such as springs, screws, and welding electrodes must meet high-quality standards. Inferior components can lead to premature wear, misalignment, and reduced machine life, regardless of how well the primary structure is designed.
Mechanical design and ergonomics
A foot-operated steel bar butt welding machine relies heavily on its mechanical design for both performance and longevity. Ergonomic designs that distribute pressure evenly across the welding electrodes help reduce stress on individual components. Machines with reinforced frames and well-balanced foot pedals experience less deformation, vibration, and fatigue over prolonged use.
Proper mechanical alignment ensures that the welding surfaces make consistent contact, which reduces uneven pressure on moving parts. Misaligned machines may experience accelerated wear on the electrodes, joints, and frame, significantly reducing overall durability.
Frequency and type of usage
The operational environment and workload of a foot-operated steel bar butt welding machine also influence its lifespan. Machines used for heavy-duty industrial tasks are more susceptible to wear than those used intermittently. Overloading a machine or operating it continuously without sufficient breaks can strain mechanical components, reduce electrode life, and increase the risk of malfunctions.
Conversely, machines employed for lighter tasks with consistent maintenance routines tend to maintain structural integrity longer. It is essential for buyers to match the machine specifications with their expected usage levels to maximize durability.
Maintenance practices
Regular maintenance is a cornerstone in prolonging the life of a foot-operated steel bar butt welding machine. Machines that are cleaned, lubricated, and inspected frequently exhibit fewer mechanical failures and maintain performance over time. Key maintenance activities include:
- Lubricating moving parts such as foot pedals, pivot joints, and alignment rods to reduce friction.
- Cleaning electrodes and contact surfaces to prevent oxidation or metal buildup.
- Tightening loose components to ensure proper alignment and prevent excessive vibration.
- Replacing worn parts promptly to avoid cascading damage to other components.
Neglecting maintenance can accelerate wear and lead to costly downtime, directly affecting the machine’s operational life.
Welding environment conditions
The environment in which a foot-operated steel bar butt welding machine operates significantly impacts its durability. Machines used in dusty, humid, or corrosive environments experience faster degradation of mechanical and electrical components. Moisture can cause rusting of metal parts, while dust and debris can obstruct the smooth movement of foot pedals and electrodes.
Operators should consider using protective covers, regular cleaning schedules, and controlled environments when possible. Environmental factors, if ignored, can lead to irreversible damage and shorten the machine’s lifespan.
Operator skill and handling
The skill level of operators affects the mechanical integrity of a foot-operated steel bar butt welding machine. Improper handling, such as pressing the foot pedal too forcefully or misaligning steel bars during welding, can place undue stress on the machine. Skilled operators who follow proper alignment procedures and maintain consistent operating pressure help reduce mechanical fatigue and wear.
Training personnel on best practices for operating the machine is an investment that contributes directly to long-term durability. Clear operational guidelines, combined with supervision, can prevent accidental damage and extend the service life of the equipment.
Quality of electrical and welding components
Electrical and welding components, such as power supply units, welding electrodes, and control circuits, play a crucial role in the durability of a foot-operated steel bar butt welding machine. Machines with stable electrical systems ensure consistent welding energy, preventing overheating or overloading that can damage mechanical parts.
Frequent replacement of low-quality electrodes or improper installation can lead to uneven welds, excessive pressure, and premature deterioration of the welding mechanism. Choosing high-quality, compatible components is essential to maintain machine longevity.
Maintenance schedule and preventive measures
Implementing a structured maintenance schedule can greatly enhance the durability of a foot-operated steel bar butt welding machine. Preventive measures, such as periodic inspections, realignment of mechanical parts, and calibration of welding settings, reduce the risk of unexpected breakdowns. A preventive maintenance approach minimizes downtime and ensures that all components operate within their design limits.
Preventive strategies may include:
- Scheduled electrode replacement based on usage cycles.
- Frame inspection for signs of stress or cracks.
- Foot pedal calibration to ensure uniform pressure application.
- Lubrication of pivot points to prevent friction and wear.
By adopting preventive practices, operators can extend the machine’s functional life while maintaining consistent weld quality.
Impact of load capacity and machine limitations
Every foot-operated steel bar butt welding machine has a rated load capacity. Exceeding this limit can accelerate wear on critical components, including the frame, electrodes, and foot pedal mechanism. Machines consistently used beyond their design limits experience increased stress, deformation, and eventual failure.
Buyers must carefully consider their steel bar sizes, welding frequency, and operational demands when selecting a machine. Adhering to manufacturer-recommended specifications ensures that the machine operates within safe limits, promoting long-term durability.
Corrosion and protective measures
Corrosion is a silent factor that reduces the durability of a foot-operated steel bar butt welding machine. Exposure to humidity, water, and chemical agents can gradually weaken metal components, particularly if maintenance is neglected. Protective coatings, anti-corrosion sprays, and proper storage practices help mitigate corrosion risks.
Regular inspection for rust and timely treatment of affected parts prevents further damage and maintains the machine’s structural integrity over time.
Summary
The durability of a foot-operated steel bar butt welding machine depends on multiple interrelated factors, including material quality, mechanical design, operator skill, maintenance practices, environmental conditions, and proper usage.
Investing in high-quality materials, precise manufacturing, and routine preventive maintenance directly correlates with improved durability. Additionally, providing a clean operating environment, training operators, and respecting the machine’s load limits further enhances longevity. Recognizing and addressing these factors ensures that the foot-operated steel bar butt welding machine remains a reliable and efficient tool in any industrial setting.