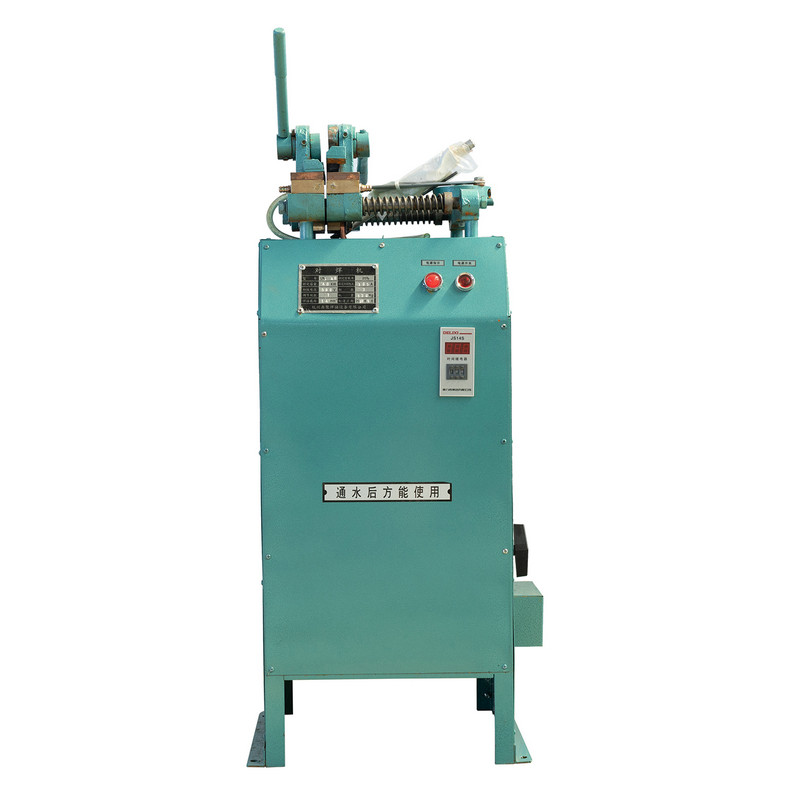
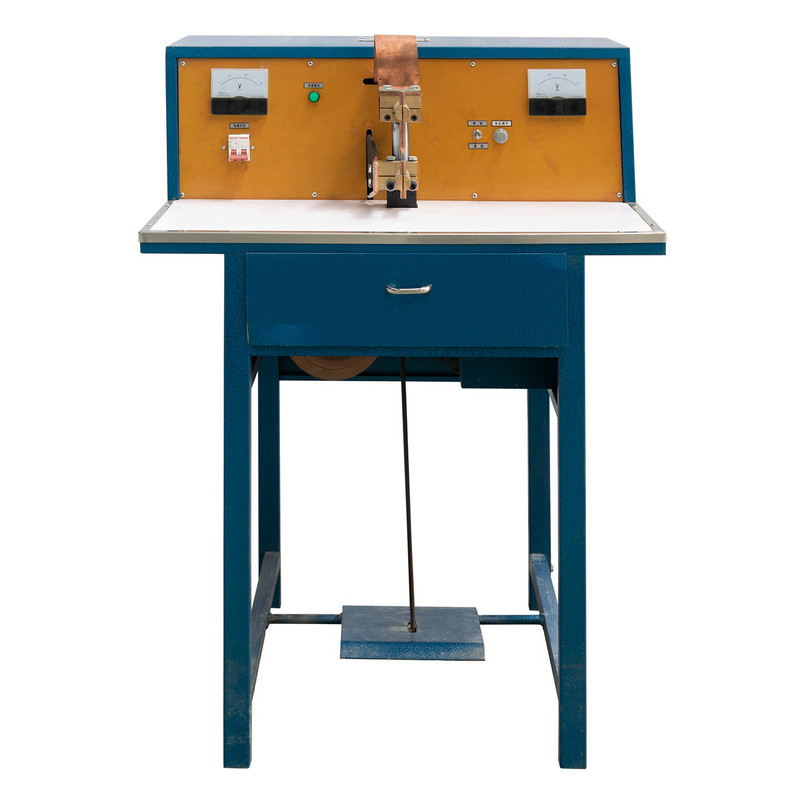
The welding industry has steadily evolved from traditional manual methods to more advanced, automated solutions. Among these, the Stable Workpiece Clamping Pneumatic Butt Welding Machine has emerged as a widely adopted choice for industries that prioritize precision, efficiency, and consistency. At the heart of this transition lies a crucial comparison: how does pneumatic clamping differ from manual clamping, and what impact does this have on production outcomes?
Understanding Butt Welding and Clamping Requirements
Butt welding is one of the most common joining methods in industrial manufacturing. It involves welding two workpieces end-to-end, creating a permanent joint that withstands high stress. The clamping mechanism plays a critical role, as it ensures that workpieces remain stable and aligned throughout the welding process.
- In manual clamping systems, the operator tightens clamps by hand, relying on skill and effort to achieve stability.
- In a Stable Workpiece Clamping Pneumatic Butt Welding Machine, air pressure automates the clamping process, delivering uniform force and reducing reliance on manual adjustments.
The clamping stage is decisive for weld quality. Any misalignment or instability can cause joint defects, leading to rework or reduced durability.
Key Characteristics of Manual Clamping Systems
Manual clamping has been used in welding operations for decades and continues to serve in smaller workshops or where low-volume production is sufficient. Some notable characteristics include:
- Operator-dependent stability: The strength and precision of the clamp rely on the skill and effort of the welder.
- Time-intensive setup: Aligning and tightening clamps manually often requires multiple adjustments.
- Cost-effectiveness for small-scale use: For limited operations, manual systems can be economical in terms of initial investment.
- Limited repeatability: Variability in operator handling may cause inconsistency across welded joints.
While manual clamping remains functional in certain contexts, it often struggles to meet the precision and speed demanded by larger-scale or quality-driven industries.
Core Advantages of Pneumatic Clamping in Welding
The Stable Workpiece Clamping Pneumatic Butt Welding Machine addresses the challenges associated with manual systems by introducing automation through pneumatic force. Its key advantages include:
- Uniform Clamping Force: Pneumatic systems apply consistent pressure, minimizing the risk of uneven joints.
- Reduced Operator Fatigue: Less manual effort means greater efficiency and improved worker safety.
- Improved Alignment: Automatic clamping ensures stable positioning of workpieces.
- Faster Cycle Times: Clamping and unclamping are quicker, allowing for higher production output.
- Scalability: Well-suited for industries that require mass production or repeated welding cycles.
These features make pneumatic clamping machines highly valued by industries focused on both quality and productivity.
Comparative Analysis: Pneumatic vs. Manual Clamping
To better illustrate the differences, the following table outlines major comparative points:
| Aspect |
Manual Clamping System |
Stable Workpiece Clamping Pneumatic Butt Welding Machine |
| Clamping Force |
Dependent on operator strength |
Uniform and consistent |
| Setup Time |
Longer, requires multiple adjustments |
Faster, automatic alignment |
| Repeatability |
Variable, influenced by operator skill |
High consistency across cycles |
| Operator Effort |
Physically demanding |
Minimal effort required |
| Productivity |
Limited to small-scale tasks |
Suitable for medium to large-scale production |
| Weld Quality |
Risk of misalignment and defects |
Enhanced precision and durability |
This comparison highlights why pneumatic systems are gaining preference, especially where high standards are non-negotiable.
Practical Applications of Pneumatic Butt Welding Machines
The Stable Workpiece Clamping Pneumatic Butt Welding Machine finds applications across multiple industries due to its precision and adaptability:
- Pipe and Tube Manufacturing: Reliable alignment ensures strong, seamless joints.
- Sheet Metal Fabrication: Uniform clamping minimizes warping during welding.
- Automotive Components: Consistency is critical for safety and performance parts.
- Construction and Infrastructure: High-quality joints improve structural reliability.
- Electrical and Mechanical Equipment: Ensures accuracy in delicate assemblies.
By reducing variability, pneumatic clamping machines improve not only product quality but also overall manufacturing efficiency.
Buyer Considerations When Choosing a Clamping System
Wholesalers and buyers must evaluate several factors before selecting between manual and pneumatic systems. Important considerations include:
- Production Volume: High-volume operations benefit more from pneumatic solutions.
- Precision Requirements: Applications demanding accuracy require stable pneumatic clamping.
- Workforce Efficiency: Reducing operator fatigue enhances workplace safety and productivity.
- Budget Allocation: Manual systems offer lower upfront costs, while pneumatic machines provide long-term value through reduced defects and rework.
- Maintenance Needs: Pneumatic systems require routine maintenance but are designed for extended durability.
Understanding these aspects allows buyers to align their investment with long-term operational goals.
Long-Term Value of Pneumatic Clamping Systems
While the initial investment in a Stable Workpiece Clamping Pneumatic Butt Welding Machine is higher than manual alternatives, the long-term benefits often outweigh the costs. These include:
- Reduced Material Waste due to fewer defective welds.
- Enhanced Productivity with faster turnaround times.
- Improved Worker Safety through minimized manual handling.
- Consistent Quality Standards that support industry compliance.
For wholesalers, these machines represent a product with strong appeal to industrial buyers seeking reliability and efficiency.
Challenges and Limitations of Pneumatic Clamping Machines
Despite their advantages, pneumatic systems are not without considerations:
- Higher Initial Cost: Not always suitable for workshops with limited budgets.
- Dependence on Air Supply: Requires access to compressed air infrastructure.
- Maintenance Requirements: Air filters, hoses, and valves need periodic attention.
Recognizing these factors ensures informed decision-making and helps buyers plan for proper implementation.